-
What Are Hot Spots?
Hot spots are regions of extreme heat that influence solar cells by absorbing energy rather than producing it.
As a result, the panel gets heated and overloaded, which leads to a short-circuit that lowers output efficiency overall while hastening material deterioration.
-
Causes of Hot Spots
We have direct experience of how cheap, subpar panels placed by low-cost installers frequently result in a failure to act on quality assurances and unforeseen problems.
The following have been known to increase the likelihood of causing hot spots:
- Overloaded regions can result from improper handling of silicon cells or inadequate soldering, while damage sustained during installation or shipping might result in microfractures.
- When cells with various currents are linked in series, cell mismatching may happen. High temperatures can result from cells with greater currents seeking to move more energy through cells with less capacity.
- Roof issues with trees or other vegetation partially obscuring solar panels. Even when one cell in a module that produces current is shaded, the other cells in the module continue to function. There must be a place for that extra power to go, and that’s where a hot spot may appear.
Hotspots are caused by a multitude of factors and can be classified as either functional or operational.
Functional causes can further be divided into two parts:
- Cell mismatch: This happens when various current-generating cells are joined in succession.
- Damaged or low-quality solar cells: This might happen during production as rolling, handling, and transporting of silicon cells are demanding activities.
The operational causes for hotspots are related to the design and operation of the photovoltaic installation, and may include:
- Shadows on solar panels: I In portrait-installed modules, if there is a shadow because of the short pitch distance between the tables, the lower row of cells will be systematically shaded in the morning and at night throughout the seasons. Installing the panels horizontally might be a feasible option since it would enable the bypass diodes to be operated at crucial moments, guarantee power generation, and reduce the creation of hotspots.
- Short Circuit: Hotspot with one or more substring open circuit failures. Potentially induced degradation (PID), mismatch, or cell breakage are frequently mistaken for one or more substrings.
- Open Circuit: It could be brought on by a module junction box or cell connector experiencing a loss of connection.
- PID: Compared to other panels, the entire panel surface is uniformly heated. PID affects might be the cause of it.
- Partial shading: Trees or vegetation may be the culprit.
- Dust and sand: Over the course of their service life, photovoltaic panels may get unclean from dust, suspended sand, dirt, and other contaminating pollutants. By visiting the site on a regular basis, the maintenance firm should be able to spot problems that need cleaning. The amount of cleaning required will mostly rely on the weather, the surroundings of the park, their topography, and whether or not the solar panels have drainage corners.
-
Consequences of Hot Spots to your Solar System
When building a solar system, it’s possible to take short cuts that initially appear to save time and money but ultimately result in a host of costly problems that have an impact on the performance of the panel’s electricity, the lifespan of the cells, and your wallet.
Hot spots that produce excessive power and heat in a concentrated region can cause cell splitting, solder to melt, or even the destruction of the entire solar cell.
The protective glass is frequently broken by hotspots as well, which will probably cause the system to shut down since moisture influences the electrical circuit. In the worst situation, ongoing insulating material degradation and softening might potentially lead the module to catch fire.
-
Avoid Hot Spots Like the Plague
First and foremost, make sure you get a system from a business that employs high-quality components and exercises extreme caution when developing and installing systems. You can request to view warranties, licences, and documentation of the manufacturing process’ openness.
A good supplier will be aware of the effects of possible shadowing and should offer a thorough assessment of the prospective environment. We can provide you a thorough analysis so you can decide how trees, poles, or tall structures may shadow your property throughout the day.
The majority of high-quality installers, like Omega Solar & Batteries, inspect each solar panel they instal while taking special care with the systems. In order to handle environmental concerns, installers should also give you a maintenance and care package that is frequently planned.
Additionally, if you believe that a low-outputting solar system you purchased has a hot spot problem, you can ask the solar sales business you bought it from to do electroluminescence imaging (EL). This works like an X-ray in that it can find cell damage including tiny fractures, hotspots, and uneven soldering that aren’t visible to the human eye.
A neglected issue is the impact of the sand on the margins.
The cells in the corners of the panels are clearly shown in the image below as being impacted by the buildup of dirt. Looking at the thermographic camera image, we can see that several of the cells in the bottom right-hand corners of the panels are significantly hotter than the rest of the cells, creating a hotspot that, if not addressed in a timely manner, may lead to issues.
NOTE: Choose solar panels with corner drains to prevent dirt build-up such as the examples below.
-
What do Hotspots Look Like?
On the surface of the panels, hotspots can occasionally be seen as dark stains or obvious damage. However, hotspots are frequently invisible to the naked eye.
But just because you can’t see something doesn’t mean it’s not there!
Thermography, which emphasises the hot patches, is the best method for finding hotspots.
Detecting hotspots with thermographic pictures
How do most customers, who lack access to this equipment, learn that a problem is developing?
For this reason, it’s important to regularly check each panel’s energy production and keep an eye out for any variations in the generation.
-
How Can Hotspots be Prevented?
The damage caused by hotspots is frequently serious enough to call for panel replacement.
Thankfully, hotspots may be avoided and their impact reduced. This is how:
1. Checking the Area
Prior to installation, a detailed analysis of the site is essential.
It will make it easier for installers to locate any obstacles that might cause the panels to throw shadows, such as trees, plants, water tanks, electricity wires, etc. Module-level smart electronics can be employed when shading cannot be avoided. These gadgets increase the PV system’s performance in situations like shade by extracting the greatest yield.
The developers will also benefit from a thorough analysis of the weather patterns in the area. Extreme weather is more common in some places (frequent lightning storms, hailstorms, or snow). Here, the installers might suggest a particular brand of modules that have been thoroughly tested in these circumstances.
2. Consistent Maintenance
A dirty panel will not only provide less electricity but also put more hotspots at danger. The panels must be cleaned once every two weeks as a result. Make sure to keep it clear of any leaves, clutter, and bird droppings.
3. Panels With Efficient Designs
Invest in high-quality panels that have hotspot management features like bypass diodes and take shading or soiling into account while designing them.
In order to maximise the number of cells protected by a single diode, Canadian Solar, a leading worldwide manufacturer of solar panels, produces panels with a half-cut cell design. These design decisions reduce the hotspot’s temperature and danger.
Always seek for effectively built panels with improved shade tolerance and lower hotspot temperatures when you research solar systems.
4. Permit Air Flow Below Modules
The temperature of the panel has an indirect relationship with power generation in solar PV systems. A solar plant’s energy output decreases under extremely hot conditions.
In solar systems, appropriate ventilation and good circulation are crucial because hotspots form as a result of overheating. It is important to provide ample room between and beneath panels when installing solar panels on rooftops.
Industrial solar systems often place panels on sheet roofing, which absorbs heat considerably more quickly. Because of this, one must constantly make sure that there is sufficient space between the panels and the tin shed. Heat pockets may be prevented by making room for air movement, which greatly lessens the consequences of hotspots.
One can also spend money on integrated solar systems like Ornate InRoof to prevent the chance of solar panels overheating. The building serves as a main roof, enabling airflow below and producing more energy.
5. After Installation, Complete Site Inspection
We now know that treating modules roughly during installation or shipping might cause internal damage. These minor dings, scuffs, or microcracks might develop into significant issues later on.
Consequently, a thorough site investigation is required. Thermography and electroluminescence imaging (EL) enable developers to look for potential danger factors.
PV testing equipment
- Damp heat test chamber.
- EL imaging camera.
The article discusses a variety of defence strategies for photovoltaic (PV) systems against abnormal events such electric shock, overcurrent, voltage swings, and hot spots. The performance of the panel may be hampered by hot spots, a well-known fault that appears in badly matched series-connected cells. Hot spots are frequently handled using active bypass switches like Schottky diodes, passive bypass diodes such power field-effect transistors (FETs), and the associated control circuitry. These techniques have several limitations and do not totally protect the cells from hot areas. In order to identify and eliminate hot spots, the study recommends a unique technique that employs a two-state relay for each string of the panel and bypasses and opens the string in the event of a mismatch. A hot spot detecting unit that employs a novel algorithm that can distinguish between partial shade and other typical irradiance variations issues the trigger commands for the relays. The paper indicates that EDCI of the PV systems significantly rises when a hot spot occurs. The proposed approach is based on an increase in equivalent DC impedance (EDCI) of the strings in hot spot situation.
Hotspot Effect on Solar Panels: Causes and Solutions
Sunlight is required for solar PV systems to create electricity. The semiconductor material used to make the panels generates power when photons interact with the surface and excite electrons.
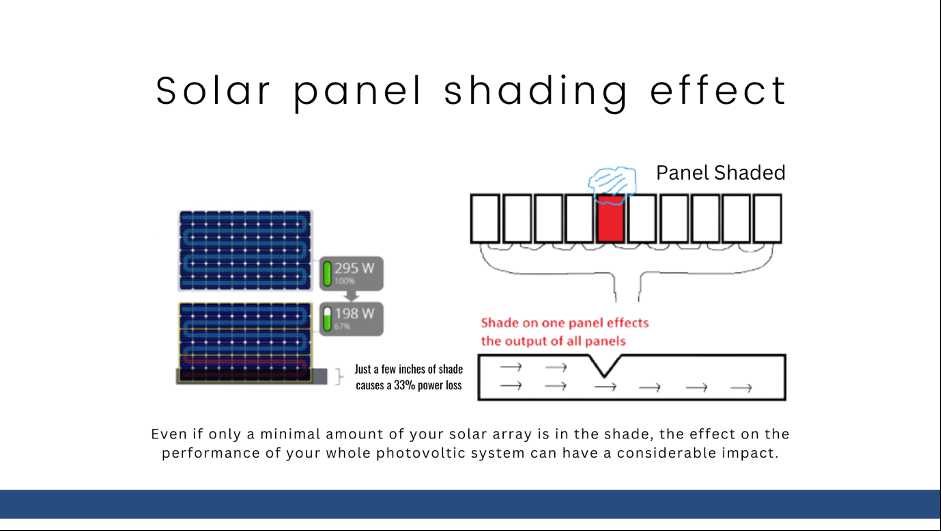
A solar panel’s cells or clusters cannot generate electricity if they are unable to receive light. The number of inoperative cells, however, will not directly correlate with the decrease in the panel’s ability to produce energy. A weak cell or group of cells will have an impact on the energy production of all the cells on the same string since solar cells are linked in series. Manufacturers will utilise bypass diodes, which let current to flow around weak cells, to stop this from happening. The construction of solar panels varies, though. Under various shading situations, the same solar panel will perform better with four bypass diodes in four strings than it will with two bypass diodes in two strings. The more bypass diodes a solar array has, the less shading-related issues it will have. But shade has other effects besides only a reduction in energy output. There is one additional issue that has the potential to seriously compromise safety and result in financial loss. In this essay, we will examine the hotspot effect.
The hotspot effect is what?
When a solar panel is shaded and the current cannot flow around weak cells, the hotspot effect happens. Eventually, the current will concentrate in a small number of cells, overheating and perhaps melting them.
One of the most frequent reasons for solar-panel failure or a fire danger is the hotspot effect. Therefore, it is crucial to employ bypass diodes when building photovoltaic systems so that current may flow through weak cells and shading effects are reduced under diverse shading circumstances.
As PV module technology advances to thinner wafers, which are prone to producing micro-cracks throughout the processes of production, shipping, and installation, hotspots are still relatively prevalent in today’s PV modules. This situation is expected to persist.
How can solar panels get hot spots?
A solar panel’s current is not distributed equally across all of the photovoltaic cells when it is shaded. The healthy cells will draw current from the weak ones in the shade.
Heat is the physical manifestation of this power loss. Reverse bias that is greater than a cell’s breakdown voltage causes the cell to get hotter and has an effect on neighbouring cells.
Thermal stress and hotspots are eventually caused by this scenario. These hot patches heat up neighbouring cells, which significantly reduces output power.
Are solar panel hotspots visible to the unaided eye?
Unless there is a clear colour difference, like a brown patch on the solar panel, hotspots are not apparent to the human eye. The hotspot may not be visible, but that doesn’t imply it isn’t there.
In order to establish how much electricity is being produced by each module, the efficiency of solar PV systems needs be continuously examined.
Without a specific measuring method, it is impossible to effectively identify the majority of hotspot issues. Thermography is the most effective method for locating hotspots.
This method allows for the capture of thermographic pictures of solar panels in order to identify any hotspots that require attention.
A photo or video that displays the temperature distribution of things is referred to as a thermographic image. Thermography has a very high accuracy rate for detecting hotspots on the surface of solar panels during examination.
What are the potential hotspot-producing sources?
Solar modules frequently have hot patches on their surface, which contribute significantly to the power consumption of the module.
At this time, we are aware that cast shadows are what produce hotspots. What then are the origins of the thrown shadows?
A solar panel may be shaded by a nearby or above-ground item, such as a tree, a person, or some machinery. Another frequent reason is a blockage caused by grit and other material on the glass surface, which stops light from reflecting and entering the cell.
Hot spots may also result from design flaws in so-called multi-crystalline or poly-crystalline silicon cells.
The hot spots can significantly affect nearby cells and impair/damage solar power output if they are not discovered in time.
How can hotspot issues on solar panels be avoided?
There isn’t much you can do to correct hotspots that already exist on solar panels. Due to the nature of these flaws, malfunctioning cells overheat and deteriorate to the point where the entire solar panel is harmed.
However, there are several measures that can be taken to prevent and avoid hotspots and their negative effect on solar panels.
Effective design matters: Hotspot issues are usually taken into account in good solar panel design. Hotspots can be caused by poor design, especially if you have a big, flat rooftop with little shade options.
In order to avoid making these errors on their own, those who build their own solar panel systems should always seek professional advice.
Preserve a healthy airflow: Hotspots do not suddenly appear. They always originate from heat accumulation, which can happen for a variety of reasons. However, you run a larger risk of hotspots developing if your solar panel system has little airflow, such as a protective cover.
To prevent the panels from overheating, a good solar panel system will constantly make sure that there is enough ventilation and airflow. Installing a power optimizer, which automatically lowers electricity output when temperatures get too high, is the best approach to avoid overheating.
By doing this, you can maintain your output levels without having to apply any manual controls.
Utilize bypass diodes: Even the formation of hotspots may be prevented by using bypass diodes on each solar panel. The absence of bypass diodes frequently results in hotspot effects on solar panels. Bypass diodes preserve power production by allowing current to flow in the event of a fault or shading.
Glass and back sheet with excellent thermal characteristics: Additionally, rather of just absorbing the heat, manufacturers can choose glass varieties that have certain characteristics that help limit the heat accumulation. In order to help the panel disperse heat more effectively, it is also a good idea to utilise a back sheet material with excellent thermal conductivity.
Removing grime and dust: A solar panel that is unclean or dusty will probably produce more hotspot effects. The impact can be lessened by routinely cleaning the panels.
A smart suggestion is to watch out for any trees, leaves, or other anything that can eventually prevent sunlight from reaching your solar panels.
Use a solar tracking system: Solar tracking systems actually move solar panels to face the sun, instead of just letting them sit in one position.
These systems constantly expose your panel to direct sunshine throughout the day, minimizing hotspot impacts. The drawback is that these tracking systems are pricey and will raise your electricity output expenses because this system typically requires more moving components.
Install the panels at a proper angle: By installing solar panels at the proper angle, you can lessen the consequences of hotspots. Online resources can help you choose the right angle for your area.
Install the panels without any obstacles: By putting your panels without any impediments, you may easily and effectively decrease hotspot impacts. This implies that they shouldn’t be too near to one another or in anything else’s shade because doing so will probably cast shadows on one another.
The two types of impediments to be on the lookout for are trees and buildings. It would be beneficial to install your panels away from any shadows.
Read the manufacturer’s guidelines: Last but not least, reading the manufacturer’s advice is strongly advised. The manufacturer will often give instructions on how to maximize the performance of their product because they are aware of what makes it operate flawlessly and optimally.
Are there any panels available that don’t have hotspots?
A few businesses have succeeded in producing hotspot-free or at least hotspot-reduced panels.
However, there is some debate about whether these products can truly be described as 100% hotspot-free. It’s sometimes only feasible to minimize hot-spotting by a certain amount, even with advances in technology.
Conclusion
As we’ve seen, there are many different reasons why solar panels develop hotspots, and most of these reasons are preventable. By selecting high-quality solar panels with built-in drainage corners, attempting to stay out of shadows, and putting strong O&M procedures in place, hotspots may be reduced and the photovoltaic system can work to its maximum potential.
Speak with our team to learn more about anomaly detection and the ways that AI may assist to lessen their effect as well as their frequency.