Solar panels use sunlight to generate power or heat. Photovoltaic cells, which make up solar panels, have the potential to generate electricity thanks to the photovoltaic effect. Solar panels are a great long-term investment for many businesses, farms, and residences. You must first understand the lifespan of solar before choosing whether it is the best option for you. This article will show you how to prolong the life of your solar panel and explain how a solar system may survive for a certain amount of time.
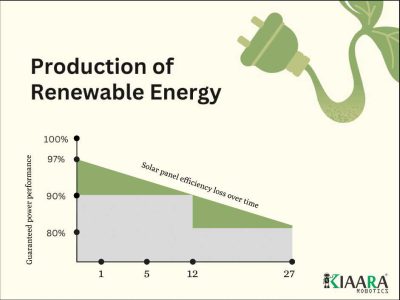
The performance of solar panels can be guaranteed for up to 25 to 30 years. But with regular maintenance, your solar panels will probably continue to provide energy for a lot longer. The first 25 to 30 years following installation are considered a solar system’s “useful life.” But solar panels may continue provide power decades after they were installed. At 60 years old, the first modern solar panel in the world is still generating electricity. It’s important to keep in mind that just because your solar panels are predicted to last a few decades, doesn’t imply they will cease producing power. Simply put, it indicates that they will produce less energy. The degradation rate of a solar panel, which gauges the decline in power production over time, establishes how long it will last.
Two different warranties are often offered by panel makers. The first is a warranty on the item, and the second is a warranty on the electricity. The anodized aluminium frame, the glass covering the panel’s top, the junction box with IP67 rating, the solar cells, and connections are all covered by the product warranty. The standard warranty you receive when purchasing a new product is fairly similar to the product warranty. On the other hand, linear power warranties take into consideration the solar panel’s deterioration over time. The majority of manufacturers offer a warranty on the solar panel’s power output.
The manufacturer determines the length of the product warranty and linear power warranty. The majority of Tier 1 module producers, including Jinko Solar, Trina, and JA Solar, provide solar panels with a 25-year linear power warranty in addition to a 12-year product warranty. Most warranties promise that after 25 years, panels will operate at least 80% more efficiently than they were designed to. According to an NREL research, the majority of solar panels continue to provide electricity after 25 years, but with somewhat lower output.
Long-term investment is necessary for solar energy. Although the initial cost may be expensive, the investment will eventually pay for itself through tax credits and monthly energy bill reductions.
Determining the lifespan of your panels is a crucial factor for anybody wanting to invest in solar energy. In this process, the question “What is the estimated lifespan of solar panels?” frequently comes up.
Let’s try some math: Solar panels have a fairly long lifespan, but it’s crucial to remember that as time passes, their efficiency may decrease at a rate of 0.5% to 1% year. This means that once a 25-year guarantee has expired, the panels should continue to produce energy at a rate of 75-87.5% of their initial rate. For instance, at the conclusion of a 25-year guarantee, a 300 watt panel need to provide at least 240 watts (80% of its rated output). Some businesses boast 30-year warranties or 85% efficiency, but these are the exceptions. 25 years at 80% efficiency is the norm. Solar panels also have a separate workmanship warranty, to cover any manufacturing defects, such as a faulty junction box or frame. Typically the workmanship warranty is 10 years, with some manufacturers offering a 20 year workmanship warranty.
What is Solar Panel Degradation?
Solar panels, like the majority of equipment, do not function at 100% after their typical life duration and finally quit working after 30-35 years. As they get older, they gradually produce less power. Degradation is the name for this action. Most solar panels’ manufacture warranties change as they become older because of degradation.
A solar panel with a reduced deterioration rate will produce more energy during its lifetime. The solar panel performs better the lower the rate of deterioration. The brand has an impact on how quickly solar panels depreciate. As you may expect, higher-quality panels will age more slowly than lower-quality ones.
The degradation rate measures how quickly solar panels lose their effectiveness over time. After ten years, a panel with a 1% annual deterioration rate will be 10% less effective.
In actuality, less than 1% per year of the systems that were examined had a deterioration rate. In other words, about 4 out of 5 solar panels are still operating at 75% efficiency or above after 25 years of operation.
The secret to increasing your solar panels’ energy output is to select panels with a reduced deterioration rate. This implies that the panel will continue to generate more energy as it gets older. Also influencing the deterioration rate is the brand of the panel, with higher-quality panels often deteriorating more slowly than lower-quality versions.
Why does solar panel efficiency drop?
Three factors may be used to separate the primary cause of solar panel damage over time.
- Light induced degradation (LID)
- Potential induced degradation (PID)
- Aging related degradation
A solar panel’s efficiency can decline within hours of being used, much like how a new automobile starts to lose part of its value the instant you drive it off the lot. This process, called Light-Induced Degradation (LID), is brought on when the solar panels’ boron layer oxidises and partly obscures the panels. Within hours of a solar panel’s first exposure to sunlight, this blockage can reduce its effectiveness by anywhere between 1 and 3 percent, but it stops at this point.
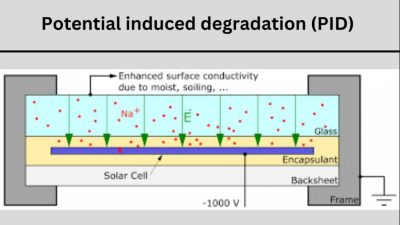
Solar panels may eventually be affected by Potential-Induced Degradation (PID), a more recent phenomena. Although the precise mechanics are yet unknown, electrical leakages from the solar panel caused by excessive humidity and salt build up can cause it to arc back and sustain damage. The good news is that because of the way our electrical networks are built, this issue is uncommon in the United States and is lessened. Working with a skilled solar installation is essential to reducing the danger of it happening to your system, but it is still a possibility.
- Light-induced degradation
When a solar panel is initially exposed to solar radiation, it experiences light-induced deterioration, which reduces its efficiency by about 1 to 3%. Throughout the lifespan of the solar panel, there is a one-time efficiency loss that cannot be prevented.
The panel’s exposure to light can result in several types of mechanical and chemical deterioration, including:
- Light-induced degradation (LID): interaction between the panel’s crystalline silicon cells and the environment outside. LID may last a few days or longer.
- Direct light-induced degradation (DLID): During the early setup phase, direct sunlight exposure can cause the photovoltaic cells’ circuitry to bend or distort due to the heat. DLID may persist for several hours.
- UV light-induced degradation (UVID): During the early setup phase, direct sunlight exposure can cause the photovoltaic cells’ circuitry to bend or distort due to the heat. DLID may persist for several hours.
- Potential-induced degradation (PID)
Voltage, heat, and humidity are the main contributors to potential induced deterioration. However, not all solar modules experience the PID effect. PID happens when ion mobility within the module between the semiconductor material and other module parts (for instance, the glass and frame) is driven by the module voltage potential and leakage current, resulting in a decrease in the module’s ability to produce power. By choosing Tier 1 solar panels from reliable vendors, this possible decrease in efficiency may be avoided. Solid encapsulation and diffusion barriers on the solar panels from reliable vendors will provide superior long-term protection against PID loss.
PID, unlike LID, does not necessarily impact every solar panel but can occur if various parts, such the frame and photovoltaic cells, operate at various voltages. The quantity of power the panel can transfer to the inverter is reduced as a result of voltage leakage brought on by this disturbance.
- Age-related degradation
Solar panels deteriorate over time as a result of their constant exposure to the elements. High temperatures, snowfall, ice, and rain all contribute to cell contamination, frame corrosion, and hardening of the crystalline silicon. Microcracks in the panel’s surface can also be brought on by hail, ice, dust, and sand, and if the panel’s seal is compromised, water may seep in.
Additionally, the quantity of light that the panel can convert into electricity might be decreased by shadowing due to reactions in the semiconductor materials employed in the cells.
Why is Degradation Rate Important While Choosing Solar Panels?
Solar panels have a 20–30 year lifespan before they start to deteriorate. The rate at which a solar panel loses power output over time is known as its degradation rate. The bulk of solar goods now available on the market deteriorate on average at a rate of 0.5% year.
When it comes to solar technology, even a slight drop in efficiency might significantly affect your potential for savings. You must thus research the rate of solar panel deterioration before making a purchase.
How Fast Do Solar Panels Degrade?
The average annual rate of solar panel deterioration is 1%. Like any technologies, solar panels will eventually generate less energy. Power generation decreases as a result of the deterioration rate. The average solar panel degradation rate is roughly 0.5% year, which means that a solar panel’s energy production will decrease by 0.5% annually. After 20 years, your solar panels should still be generating about 90% of their initial power.
What can I Do to Extend the Life of My Solar System?
High-quality solar panel purchases, proper installation, and routine maintenance may all assist prevent deterioration and maintain solar panels’ maximum efficiency for the duration of their useful lives.
To increase the lifespan of your solar panels, you may do the following:
Utilize a spare battery: Your solar panels won’t have to work as hard and you’ll be able to charge more gadgets at once thanks to a backup battery.
One of the major costs of off-grid systems is the maintenance and replacement of the batteries. Even low-maintenance battery types like lithium and sealed lead acid batteries require inspection on a yearly basis.
Depending on the brand, the guarantee for most batteries ranges from three to ten years. But if you don’t take good care of your batteries, they can stop working after only a year.
For instance, lead acid batteries must be fully recharged after use, and if they are left sitting for a lengthy period of time without being recharged, they may suffer lasting damage.
Depending on the battery type, how it is used, and how it is maintained, the majority of high-quality off-grid deep cycle batteries have a lifespan of 5 to 15 years. By taking good care of your batteries and making sure they are put correctly, you may increase their lifespan.
The greatest thing you can do is to correctly build your system from the beginning. To keep everything functioning properly, factor in the right amount of battery capacity, solar power, and inverter output up front.
Regular inspection: Regular inspection is necessary to find defects and possible problems. Solar panel maintenance and repair can assist prevent small problems from developing into more significant and expensive problems. You must look for damaged panels, exposed cables, drooping racks, and fractures. To achieve the finest results, the damage should be repaired by experts.
Replace Inverters After 10 Years: On grid-tie inverters, the majority of manufacturers provide a 10-year warranty, with the option to upgrade to a 20- or 25-year warranty on many models.
Extensions of inverter warranties are a prudent investment. It is realistic to anticipate that you will replace your inverter at least once before the warranty on your panels expires. In 15 years, a better and newer one will probably take its place if your inverter malfunctions.
Inquire with the inverter’s manufacturer about available options and processes for an extended warranty. For extended warranties, direct purchases must be made through the manufacturer. Currently, affordable inverter warranty extensions are offered by SolarEdge and SMA.
There are fewer warranties available for off-grid inverters. They last between one to five years, with some variants providing extensions of as long as ten years.
When obtaining an extended warranty, read the fine print thoroughly. Some only pay the cost of the components, not the labour.
This may not bother you if you plan to replace the inverter yourself. However, you could have to pay out of pocket if you subsequently determine the inverter has to be replaced.
Maintain the cleanliness of the panels: To avoid damage, the panels should be maintained clean.
For best performance and security, solar panels must be kept clean.
Accidental harm to the panels might reduce their ability to absorb sunlight. The panels’ efficiency can be decreased by dirt and debris becoming stuck in the grooves and edges of the panels and being difficult to remove due to improper cleaning methods, which can also result in the panels being damaged or broken. The inverters, which convert the DC electricity generated by the solar panels into usable AC power, are similarly susceptible to error or failure.
Additionally, consider safety. The panels might become slippery and dangerous for anybody attempting to clean them if they are left too dirty. It is crucial to exercise caution and follow the correct methods in order to ensure that the solar panels are completely cleaned without causing any accidents or injuries.
By giving solar panels the necessary maintenance on a regular basis, you can maintain them running at their maximum efficiency. To ensure that your panels are performing at their peak, clean them with the proper techniques and caution. Don’t allow these problems prohibit the correct operation of your solar system.
Arrange the panels at the right angle: The solar panels should be set up at the correct angle for the optimum results. Choose a location that receives the most sun exposure all year round.
Make use of a solar concentrator: A solar concentrator is a crucial part of a solar-powered system. To generate energy, it focuses sunlight.
End-of-Life Management for Solar Photovoltaics:
Even when the panels need to be replaced after reaching the end of their useful life as power producers, they are still valuable. Instead of dumping of obsolete solar panels in landfills, recycling enables the extraction of the majority of the valuable components and raw materials for the production of new solar panels or utilisation in other industries.
The below materials are among those that can be repurposed:
- Approximately 95% of the glass from a panel may be recycled for coatings or packaging.
- The whole metal frame, which contains aluminium, may be reused for new panels.
- Around 85% of the silicon content may be salvaged for use in solar panels, electronics, or batteries.
- Polyethylene glycol terephthalate (PET) and ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), polymers that account for 5% and 10% of the waste from a solar cell, respectively, may be recovered.
The recycling procedure is really more environmentally friendly since Chinese experts have developed a brand-new technique to extract PET and EVA without the use of hazardous solvents.
Additionally, silicon is being used more and more in lithium-ion battery anodes, which might reduce the price of raw materials in the emerging market for electric vehicles.
What is the efficiency of solar cells?
Efficiency in solar panels refers to the amount of energy generated from a given surface area. Efficiency rises when energy production increases per unit of surface area. Likewise, efficiency falls off when energy production from a given surface area rises. As solar panels get more and more efficient over time, manufacturers may increase the solar panel’s rated power output as well as its efficiency.
The rise of solar module power over the preceding 10 years is seen in the graph below. At the start of the decade, the maximum rated power of a solar panel was 295 Wp; by its end, this value had nearly quadrupled to 600 Wp.
What other factors can affect solar panel efficiency?
Other elements, in addition to the three in the preceding section, have an impact on the effectiveness of solar panels and solar plants both directly and indirectly.
These factors are discussed below.
Solar panel orientation: The solar panel’s efficiency may be impacted by the amount and angle of light that it receives. For instance, if the project is located south of the equator, solar panels angled north will provide the greatest power and energy. Similarly, for projects located north of the equator, solar panels facing south provide the maximum electricity and energy.
tch of the roof: The slope of the roof will determine how much sunlight reaches the solar panels during the day, thus affecting solar production.
Temperature: Higher temperatures can cause the solar panels’ output and efficiency to decline.
Shade: Even a slight amount of shadowing may have a major impact on a solar panel’s performance. A string of 15 to 18 solar panels is often made by joining them in series in household solar setups. Any solar panel in the string with a shadow on it has the potential to significantly reduce output and the overall efficiency of the solar plant.
Design: Design has a considerable impact on both the overall performance of the solar power plant and the effectiveness of the solar panels. When designing a solar power plant, it is important to consider the plant’s total capacity as well as its string layout, inverter count, safety measures, panel position, and panel orientation. A professional design ensures the use of the correct wires and inverter size. If cables and inverters are too large, the project’s finances may suffer, and if they are too tiny, the efficacy of solar panels may decline.
Balance of system: The solar power plant utilises balance of system components in addition to solar panels. Included in this are the mounting hardware, cables, inverters, and safety measures. To preserve the balance of the system, it is important to size and use high-quality products. Given that the solar plant’s expected lifespan is between 25 and 30, all of its components should be bought from reputable suppliers.
The aforementioned issues must be taken into consideration during the project’s design and execution. Using qualified and certified installers may considerably reduce the efficiency losses inside a solar system.
Do I need to replace my solar panels due to degradation with higher efficiency and higher power panels?
The amount of solar energy that can be stored in a panel has nearly quadrupled over the past ten years, and in the past two years, solar panels’ efficiency has grown by over 5%. It should be emphasised that solar panels’ power capacity and efficiency will continue to rise in the next years. Repowering is the process of replacing outdated solar panels with fresh ones. In significant solar projects, this is typical.
It is not advised to change the modules because a solar installation often pays for itself in less than 5 years, especially given that the majority of solar panel manufacturers provide a 25-year performance warranty.
What must you consider while installing solar panels on your roof?
Numerous factors, some of which are under our control and others which are beyond our control, impact the efficiency of solar panels. You should think about purchasing solar panels from Tier 1 providers when determining whether to install solar electricity on your roof. Tier 1, Tier 2, and Tier 3 categories are used to rank solar panel providers. Tier 1 solar panels are those that are produced by well-known, well-respected major brands. Building a solar power plant with Tier 1 suppliers rather than Tier 2 or Tier 3 is more safer. Although Tier 1 solar panels are an excellent indicator of trust and reputation, Tier 2 and Tier 3 are not always worse. One can cut down on efficiency losses within a facility by using tier 1 suppliers.
Other efficiency losses occur throughout the solar plant’s design and construction. By employing licenced solar plant installers, this loss may be reduced.
Here’s What That Means For Your ROI
That’s great news if getting a good return on your system’s investment (ROI) is your top objective.
The vast majority of solar savings calculators on the internet use a 25-year guarantee. Your panels should be able to deliver more mileage if possible.
Is it prudent to invest in solar energy? Use our Solar ROI Calculator to calculate your payback period—the time it will take for tax advantages and energy bill savings to equal the initial cost of your system.
We cannot guarantee that panels will endure beyond their warranty period, despite the fact that that is the whole point of a warranty. The majority of panels, however, continue to generate at a lesser rate well into the end of their anticipated lifespan. This occurs as a result of the lack of moving parts in solar panels, which normally have a very high level of dependability.
If your solar system is paid off and your panels keep producing after it is paid off, your ROI will be far better than what any online calculators can estimate (including ours).
Want to make it more likely that your panels will last longer than their guarantee period? Maintaining the effectiveness of your system just requires a small amount of labour.
Conclusion
Although the efficiency of solar panels does deteriorate with time, this typically happens at a rate of 0.5% to 1% every year. Solar panels can continue to provide power at a high level for 25–30 years or longer with correct installation and upkeep. Additional elements that might impact how long solar panels endure include temperature, the outside environment, and shadowing. The lifespan of solar panels is also being extended by technological advancements; some modern types have a longevity rating of at least 40 years. Solar panels are still a smart investment since they may save a significant amount of energy over the course of their lifespan, even though they do lose efficiency over time. It’s important to consider the warranty, maintenance, technical advancements, and recycling options when selecting solar panels for your home or company.